IoT for Smart Factories: The Connected Backbone of Next-Generation CNC Machining
From Automated Islands to Cognitive Ecosystems: The Smart Factory Imperative
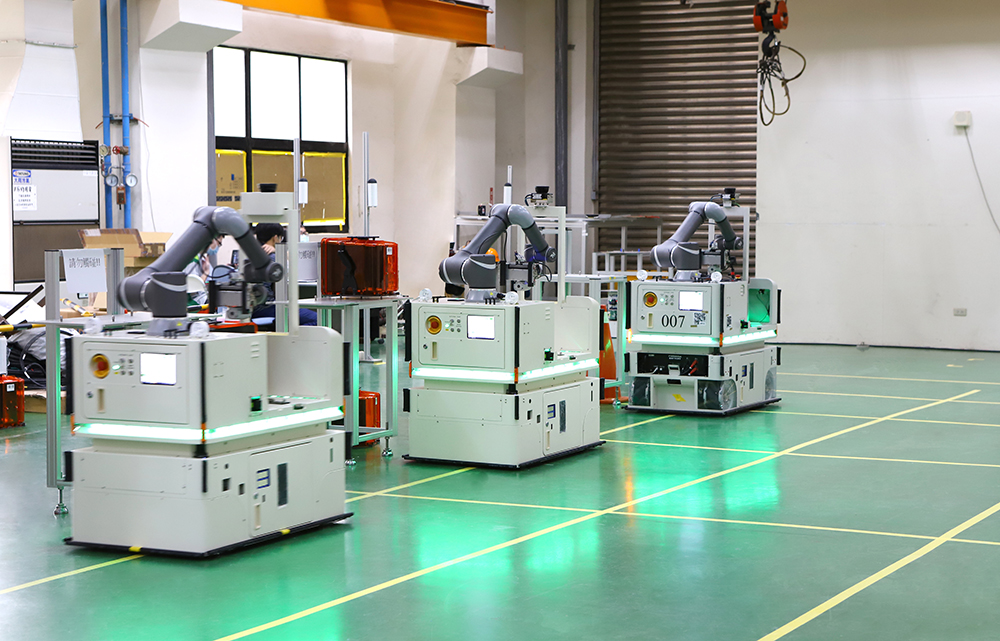
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a fundamental paradigm shift. The era of standalone, automated islands of production—where a CNC machine operates in isolation, its data siloed and its performance assessed only through post-process inspection—is giving way to the age of the integrated, cognitive smart factory. At the heart of this transformation is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). For a precision-focused CNC machining service provider like JLYPT, mastering IoT for smart factories is not a future consideration; it is the critical, present-day infrastructure that unlocks unprecedented levels of operational visibility, predictive intelligence, and agile production.
A smart factory is more than a collection of networked machines; it is a responsive, data-driven ecosystem where every asset, from the high-speed spindle to the autonomous guided vehicle (AGV), communicates and collaborates. This transition is driven by the relentless demands of modern manufacturing: the need for mass customization in High-Mix, Low-Volume (HMLV) production, the pursuit of zero-defect quality, and the imperative to maximize asset utilization and energy efficiency. IoT for smart factories provides the central nervous system that makes this possible, transforming raw machine data into actionable intelligence and enabling a leap from reactive operations to proactive, optimized control.
This comprehensive guide will explore how IoT for smart factories is revolutionizing CNC machining. We will dissect its underlying architecture, delve into the key technologies enabling machine connectivity, and quantify its impact through core applications like predictive maintenance and real-time quality assurance. Through detailed case studies and technical analysis, we will illustrate how JLYPT leverages this connected backbone to deliver superior precision, reliability, and value to our clients.
Deconstructing the IoT Architecture: The Layer-Cake of Connectivity
Implementing a robust IoT framework in a machining environment requires a structured, layered approach. This architecture ensures data flows seamlessly from the shop floor to the cloud and back, enabling real-time insights and closed-loop control.
1. The Device & Sensor Layer: The Foundation of Data Acquisition
This is the physical layer where data originates. In a CNC smart factory, it extends far beyond the machine tool itself.
-
Smart CNC Machines: Modern machining centers are evolving into smart CNC机床 (Smart CNC Machine Tools), equipped with integrated sensors and open communication protocols like OPC UA or native interfaces (e.g., FANUC FOCAS, Siemens SINUMERIK). They generate continuous data streams on spindle load, axis servo currents, feed rates, and controller alarms.
-
Ancillary Monitoring Systems: Critical supplemental data comes from specialized systems:
-
(Tool Condition Monitoring Systems): Utilize force, vibration, and acoustic emission sensors to detect tool wear and breakage in real-time.
-
(In-Process Gauging Systems): Integrated touch probes or laser scanners provide closed-loop feedback on part dimensions, enabling automatic offset compensation.
-
Environmental & Energy Sensors: Monitor coolant condition, air quality, and granular energy consumption at the device level.
-
2. The Edge Computing Layer: Intelligence at the Source
Edge computing is arguably the most critical technological advancement for IoT for smart factories. It involves processing data physically close to its source—on the machine or in a nearby edge industrial PC or gateway.
-
Function: The edge layer performs high-speed, low-latency data processing. It filters, aggregates, and contextualizes raw machine data before transmitting it upstream. For example, an edge device can analyze a vibration waveform to extract a meaningful health indicator, sending only a single value instead of thousands of data points.
-
Benefits: This reduces network bandwidth load, enables millisecond-level response for critical alerts (e.g., crash detection), and allows for autonomous decision-making even during network interruptions. It is essential for predictive maintenance algorithms that require immediate analysis of high-frequency sensor data.
3. The Connectivity & Network Layer: The Information Highway
This layer comprises the wired and wireless networks that transport data. A hybrid approach is standard:
-
Industrial Protocols & Wired Networks: Reliable, high-speed factory floor networks using Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and industrial Ethernet (e.g., PROFINET, EtherCAT) connect machines and edge devices.
-
5G & Wireless: 5G industrial private networks provide unprecedented mobility, flexibility, and low latency for moving assets like AGVs and (Intelligent Inspection Robots), enabling reliable real-time coordination and video stream backhaul.
-
(Cloud-Edge-Device Integrated Architecture): This modern paradigm, where edge and cloud computing are seamlessly orchestrated, has become the default framework. It ensures data is processed in the most efficient location, balancing speed with scalability.
4. The Platform & Application Layer: Where Data Becomes Insight
This is the software brain of the smart factory. An Industrial IoT platform (like MachineUnite or similar) ingests, manages, and analyzes the aggregated data.
-
Digital Twin & Visualization: The platform creates a digital twin—a virtual, real-time representation of the physical factory. This allows for remote monitoring via dashboards that show Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), machine states, and production progress.
-
Data Analytics & AI/ML Integration: Here, historical and real-time data are fused. Advanced analytics and machine learning models uncover patterns, predict tool failure, optimize cutting parameters, and generate prescriptive actions.
-
System Integration (MES/ERP): The IoT platform does not operate in isolation. It integrates deeply with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, turning insights into automatic work orders, quality alerts, and maintenance schedules.
Table 1: The IoT Technology Stack for a CNC Smart Factory
| Architectural Layer | Key Components & Technologies | Primary Function in CNC Machining | Outcome & Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device & Sensor Layer | Smart CNC with OPC UA, Tool Condition Monitoring, In-Process Probes, RFID, Energy Meters | Raw data generation: Position, load, vibration, temperature, dimensions, identity. | Granular visibility into the physical machining process and asset status. |
| Edge Computing Layer | Industrial Edge Gateways, IPCs, Embedded AI Processors (e.g., NVIDIA Jetson) | Local data processing, protocol conversion, real-time analytics, immediate anomaly detection. | Reduced latency and bandwidth, enables autonomous machine-level decisions and fast response. |
| Connectivity Layer | TSN, 5G Industrial Private Networks, Industrial Ethernet, Wi-Fi 6/6E | Reliable, secure, high-speed data transmission between devices, edge, and cloud. | Flexible and robust network supporting both fixed and mobile equipment in harsh environments. |
| Platform & App Layer | IoT Platform (e.g., MachineUnite, PTC ThingWorx), Data Lakes, AI/ML Models, Digital Twin, MES/ERP Integration | Data aggregation, storage, advanced analytics, visualization, system integration, and predictive insights. | Holistic operational intelligence, predictive maintenance, optimized production planning, and data-driven decision-making. |
Core Applications: Transforming CNC Machining Operations with IoT
The true value of IoT for smart factories is realized in its concrete applications that solve long-standing manufacturing challenges.
1. Predictive & Prescriptive Maintenance: From Downtime to Uptime Assurance
Reactive maintenance is a costly relic of the past. IoT enables a predictive approach.
-
How It Works: Vibration, temperature, and current sensors on spindles, ball screws, and axes feed data to edge-based or cloud-based AI models. These models, trained on historical failure data, identify subtle anomalies and degradation patterns—long before a catastrophic failure.
-
Outcome: Maintenance can be scheduled during natural breaks in production. Systems like MachineUnite go a step further into prescriptive maintenance, not only predicting failure but also diagnosing the root cause and suggesting specific corrective actions. This drastically reduces unplanned downtime, extends component life, and protects valuable work-in-progress.
2. Real-Time Quality Control & Process Optimization
IoT moves quality assurance from a post-process checkpoint to an integrated, in-process function.
-
Closed-Loop Machining: In-process measurement probes directly feed dimensional data back to the CNC controller, allowing for automatic tool offset updates within the same machining cycle. This compensates for tool wear and thermal drift in real-time.
-
Statistical Process Control (SPC) 2.0: IoT enables true real-time SPC. Every critical dimension from every part can be logged and tracked. AI algorithms can correlate quality deviations with specific machine parameters (e.g., a slight spike in vibration at a certain spindle speed), enabling engineers to continuously refine and optimize cutting recipes for superior surface finish and consistency.
3. Enhanced Asset Performance & Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
OEE is the gold standard for measuring manufacturing productivity. IoT provides the accurate, automated data to calculate it and, more importantly, improve it.
-
Automatic State Detection: IoT platforms automatically categorize machine state into Running, Idle, Setup, and Down based on spindle rotation, axis movement, and program execution, eliminating manual and error-prone logging.
-
Loss Analysis: By pinpointing the exact reasons for idle and downtime (e.g., waiting for material, programming delay, tool change), IoT analytics identify the largest bottlenecks. This data-driven insight allows managers to implement targeted improvements, systematically driving OEE upward.
4. Agile Material Handling & Logistics Integration
The smart factory extends beyond the machine tool. IoT synchronizes material flow with production flow.
-
AGV/RGV Integration: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Rail-Guided Vehicles (RGVs), connected via 5G or Wi-Fi, receive instructions from the MES. They deliver raw materials to machines just-in-time and remove finished parts, all tracked in real-time.
-
Tool & Inventory Management: RFID-tagged tool holders and raw material bins can be tracked throughout the facility. The system knows tool location, usage history, and remaining life, and can automatically generate replenishment orders when stock is low.
Case Studies: IoT in Action Across Manufacturing Sectors
Case Study 1: High-Volume Automotive Component Manufacturer
-
Challenge: A Tier-1 supplier machining transmission cases faced unpredictable breakdowns of multi-spindle machining centers, causing costly line stoppages and delivery delays. Their manual tool change schedules were either too conservative (wasting tool life) or too aggressive (risking breakage).
-
IoT Solution: JLYPT implemented a comprehensive predictive maintenance solution. Vibration and current sensors were installed on each spindle. Data was processed at the edge to extract key health indicators, which were streamed to a cloud-based AI platform. The platform learned normal operating signatures and began issuing early warnings for bearing degradation 2-3 weeks before expected failure. Simultaneously, a tool condition monitoring system was integrated to track wear based on cutting force.
-
Outcome: Unplanned downtime on the targeted line was reduced by 65%. Tooling costs were optimized by extending average tool life by 22% through data-driven change intervals. The ROI was achieved in under 8 months, and the solution is now being scaled plant-wide.
Case Study 2: Aerospace Precision Parts Job Shop
-
Challenge: This HMLV shop produced complex, high-value aerospace components. Manual job setup and in-process inspection were major bottlenecks, limiting throughput. Quality documentation for audits was a tedious, paper-based process.
-
IoT Solution: The shop deployed an IoT suite centered on digital work instructions and integrated metrology. Each machine was equipped with an edge touchscreen. At job start, the operator scanned a part QR code, which automatically loaded the CNC program and displayed setup sheets and inspection plans. A wireless in-process probe automatically measured key features post-machining, with results instantly logged to the digital traveler and compared against tolerances.
-
Outcome: Average job setup time decreased by 40%. First-part inspection time was cut by 75%, and quality documentation became 100% digital and audit-ready. The real-time OEE dashboard revealed significant idle time between jobs, leading to rescheduling that increased overall capacity by 18%.
Case Study 3: “5G Fiber-Wisdom Factory” – A Large-Scale Process & Discrete Hybrid
-
Challenge (Based on Public Model): A large chemical fiber manufacturer like “Yizheng 5G Fiber-Wisdom Factory” needed to integrate vast amounts of data from continuous process units with discrete packaging and logistics operations. They required ultra-reliable connectivity for mobile assets and massive sensor networks.
-
IoT Solution: The factory built a converged 5G industrial private network alongside a 全光网络 (All-Optical Network) backbone. This infrastructure connected thousands of sensors, 智能巡检机器人 (smart inspection robots) with 3D LiDAR, and fleets of AGVs. The robots perform autonomous patrols, collecting image and thermal data, while AGVs handle material transport—all coordinated in real-time over the 5G network.
-
Outcome: The factory achieved a fully interconnected ecosystem. Inspection efficiency soared, manual labor in hazardous areas was minimized, and material flow became seamless. The project became a national benchmark, demonstrating how IoT for smart factories powered by 5G can integrate process and discrete manufacturing into a unified, intelligent operation.
Implementing Your Smart Factory Journey: A Strategic Roadmap
Transitioning to an IoT-enabled smart factory is a strategic evolution, not a one-time project. A phased, value-driven approach is key:
-
Start with a Pilot and Clear Objectives: Identify a high-impact, contained area. For example, target one critical CNC machine for a predictive maintenance pilot. Define success metrics: e.g., a 30% reduction in unplanned downtime on that asset within 6 months.
-
Build the Foundational Infrastructure: Ensure your machines have the necessary connectivity (OPC UA, MTConnect). Deploy a robust and scalable industrial network. Selecting an interoperable, standards-based IoT platform is crucial for long-term growth.
-
Focus on Data Governance & Skills: Clean, contextualized data is the fuel. Establish protocols for data tagging and management. Concurrently, invest in upskilling your team—machinists need to become data-savvy technicians, and engineers need analytics skills.
-
Scale Applications & Integrate Systems: With the foundation set, scale successful pilots to other machines and lines. Deeply integrate the IoT data stream with your MES and ERP to close the loop between shop-floor events and business planning.
-
Embrace Continuous Evolution: The technology landscape is dynamic. Stay abreast of advancements like AI-driven agentic systems for autonomous scheduling or generative AI for troubleshooting. The smart factory is a journey of continuous improvement.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of IoT in Precision Manufacturing’s Future
The integration of IoT for smart factories is redefining the possibilities of CNC machining. It is the essential infrastructure that transforms passive machine tools into intelligent, communicative assets within a harmonized production symphony. The benefits—hyper-efficiency, guaranteed quality, resilient operations, and agile adaptability—are tangible and transformative.
At JLYPT, we have moved beyond simply operating advanced CNC machines. We are engineering connected manufacturing ecosystems. Our expertise lies in designing and implementing the practical IoT for smart factories solutions that extract maximum value from precision equipment. We partner with our clients to build this connected future, turning data into their most powerful competitive asset.
Ready to transform your manufacturing operations with a connected, intelligent approach? Explore how JLYPT’s expertise in IoT for smart factories can build a resilient, data-driven foundation for your precision machining success. Begin the conversation by visiting our comprehensive service page at JLYPT CNC Machining Services.