Beyond the Physical Arm: Unleashing the Power of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Smart CNC Manufacturing
The narrative of robotics in manufacturing has long been dominated by the image of the physical robotic arm—the relentless, precise executor of tasks on the factory floor, handling materials, welding seams, or applying paint. However, a quieter, yet equally transformative, revolution is unfolding within the digital veins of the modern factory. This revolution is powered by Robotic Process Automation (RPA) manufacturing, a paradigm that leverages software “robots” or “bots” to automate repetitive, rule-based digital tasks across business and manufacturing execution systems. For a precision-driven CNC machining service provider like JLYPT, integrating RPA manufacturing is not about replacing the machinist or the machine tender; it is about liberating human intellect from the friction of administrative processes, creating a seamless digital thread, and unlocking a new tier of operational agility and data integrity that directly feeds back into physical production quality.
This comprehensive guide explores the strategic implementation of RPA manufacturing within the context of advanced CNC machining. We will dissect its core principles, map its high-impact applications across the production lifecycle, provide a detailed technical blueprint for integration, and quantify its value through concrete metrics and real-world case studies. This is the essential guide to building a cognitive layer over your physical operations, where software robots work in concert with machine tools and human experts to eliminate errors, accelerate throughput, and deliver unprecedented traceability.
1. Demystifying RPA: The Digital Workforce for the Manufacturing Backbone
At its core, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves configuring software applications—”bots”—to emulate and execute the actions of a human interacting with digital systems and software. These bots can log into applications, move files and folders, copy and paste data, fill in forms, extract structured and semi-structured data from documents, and perform calculations. In a manufacturing context, this transcends simple office automation.
RPA manufacturing focuses specifically on the myriad of digital handoffs that surround the physical act of machining. It addresses the “swivel-chair” processes where employees manually bridge gaps between disparate, often non-integrated systems like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, Quality Management Systems (QMS), and machine controller networks.
Key Characteristics of RPA in Manufacturing:
-
Non-Invasive Integration: RPA bots interact with the presentation layer of existing software (via UI scraping, APIs, or database connectors) without requiring deep, costly, and disruptive changes to the core legacy IT infrastructure. This makes it an agile solution for integrating older CNC equipment or software that lacks modern connectivity.
-
Rule-Based and Deterministic: RPA excels at processes with clear, logical rules. If X happens in System A, then perform Y in System B. This is perfect for translating a work order release into machine setup instructions or consolidating machine runtime logs into an OEE dashboard.
-
High-Volume and Repetitive: The value proposition soars when applied to tasks performed hundreds or thousands of times, such as generating shipping labels, processing inspection reports, or updating inventory counts after a production run.
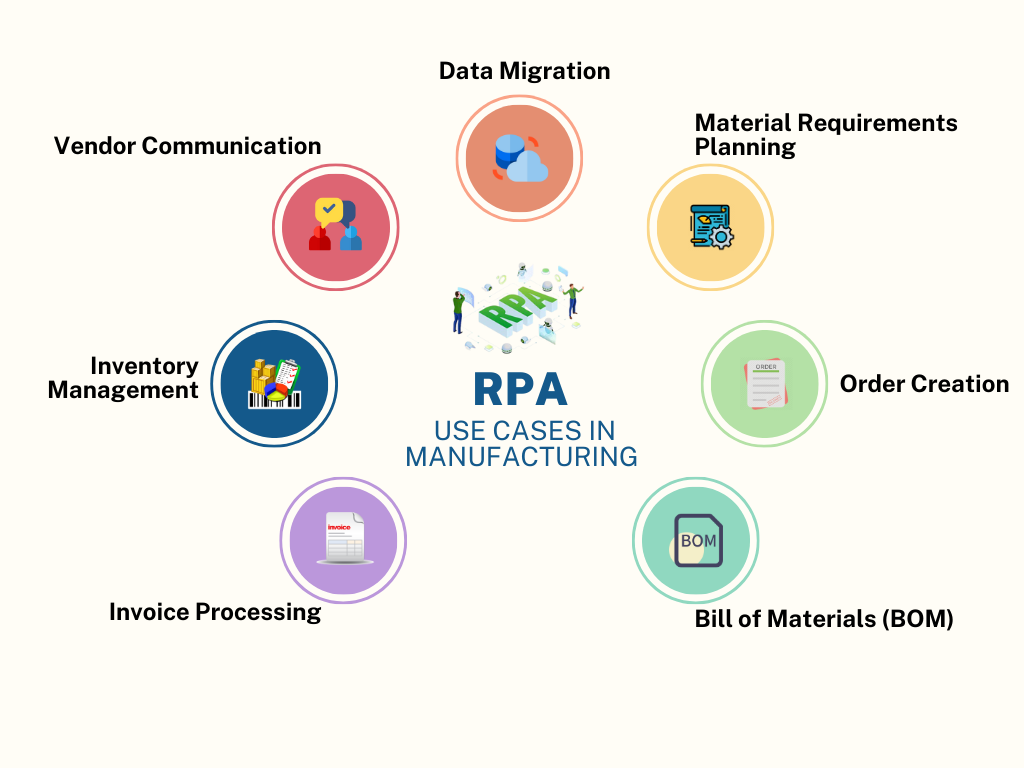
2. The CNC Machining Value Chain: Prime Processes for RPA Automation
The journey of a precision part, from order receipt to shipment, is riddled with digital process bottlenecks. RPA manufacturing bots act as the connective tissue, automating workflows across these key domains:
A. Engineering & Order Processing
-
Automated Bill of Materials (BOM) & Routing Generation: Upon order entry in the ERP, an RPA bot can retrieve the part CAD file from a PDM system, query a central tooling database for required tools, and automatically generate a detailed BOM and machining routing sheet in the MES.
-
CNC Program Management & Version Control: Bots can monitor designated network folders for new or updated CNC programs (G-code/M-code). They can automatically check them into a version-controlled repository, log the change, and notify relevant programmers or machine operators, ensuring the correct program revision is always used.
-
First-Article Inspection (FAI) Packet Assembly: Automatically collate the required documents—CAD drawing, CAM program, inspection plan, and material certifications—from various systems to create a complete digital FAI packet for the quality team, slashing preparation time from hours to minutes.
B. Production Scheduling & Machine Monitoring
-
Dynamic Scheduling & Dispatch: Integrating RPA with Andon systems or machine monitoring platforms, bots can automatically reassign work orders based on real-time machine availability (e.g., if a machine goes down for unplanned maintenance, the bot re-routes its queue to the next available machine with similar capabilities).
-
Automated Data Harvesting for OEE: Bots can log into individual CNC machine interfaces (or connect via MTConnect/OPC UA agents) at scheduled intervals, scrape runtime, alarm, and cycle count data, and populate centralized OEE calculation dashboards, eliminating manual data entry and providing real-time performance visibility.
-
Predictive Maintenance Triggering: When vibration analysis software or thermal monitoring flags an anomaly, an RPA bot can automatically retrieve the machine’s serial number, open a work ticket in the CMMS with pre-populated details, and even initiate a spare parts availability check in the inventory system.
C. Quality Assurance & Compliance
-
Automated Inspection Data Recording: RPA bots can interface with digital calipers, CMMs, and vision systems to capture measurement results directly. They can then populate statistical process control (SPC) charts, compare results against CAD nominal values, and automatically generate non-conformance reports (NCRs) in the QMS if tolerances are breached.
-
Certificate of Conformance (CoC) Generation: Upon final quality approval, a bot can pull all relevant data—part numbers, heat/lot codes, inspection results, operator stamps—from the MES and QMS to instantly generate and email a customized CoC to the customer.
-
Regulatory & Audit Trail Compliance: Bots can perform continuous, automated audits of digital records, ensuring that required signatures, program revisions, and material traceability documents are complete and linked for every job, streamlining compliance with standards like AS9100 or ISO 13485.
D. Supply Chain & Logistics
-
Procurement & Replenishment Automation: When raw material inventory falls below a threshold, an RPA bot can automatically generate and send a purchase order to a pre-approved vendor via email or EDI, and then update the ERP with the expected delivery date.
-
Automated Shipping & Logistics Coordination: Once a job is marked “Ready to Ship,” a bot can retrieve the customer’s shipping preferences from the CRM, generate shipping labels and commercial invoices, book a carrier, and send tracking information to the customer—all without human intervention.
Table 1: High-Impact RPA Use Cases in CNC Manufacturing
| Process Domain | Manual/Bottleneck Process | RPA Automation Solution | Key Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order to Production | Manual transfer of order details from ERP to MES; manual BOM creation. | Bot auto-creates MES work order with BOM & routings from ERP data. | Lead Time Reduction: Order release accelerated by 70-90%. Error Elimination: Zero data entry mistakes. |
| Machine Data & OEE | Operators manually logging runtime, downtime reasons, and piece counts on paper/Excel. | Bot harvests machine data automatically from controllers, calculates OEE. | Data Accuracy & Real-Time Insight: 100% accurate, real-time OEE visibility. Labor Savings: Frees 1-2 hours/shift for value-added work. |
| Quality Documentation | Quality tech manually transcribing CMM data into reports and CoCs. | Bot integrates with CMM software, auto-populates reports and generates CoCs. | Throughput: Inspection report generation time cut by 80%. Compliance: Ensures perfect, auditable digital traceability. |
| Inventory & Procurement | Planner manually checking inventory levels and creating POs for replenishment. | Bot monitors inventory, auto-generates and sends POs when triggers are met. | Stock-Out Prevention: Proactive, timely reordering. Process Efficiency: Reduces procurement cycle time by 50%. |
| CNC Program Management | Inconsistent program version storage; manual distribution to shop floor. | Bot manages central repository, logs all changes, pushes updates to correct machines. | Risk Mitigation: Eliminates scrap from wrong program version. Control: Centralized, auditable program management. |
3. The Technical Architecture: Building a Scalable RPA Manufacturing Framework
Successful RPA manufacturing implementation requires more than deploying a few bots. It demands a strategic architectural approach.
-
Process Discovery & Assessment: The foundation is a meticulous analysis of existing processes. Using process mining tools or detailed workflow mapping, identify candidates with high volume, clear rules, and reliance on multiple systems. Prioritize based on ROI potential and complexity.
-
Bot Development & Orchestration: Development platforms (e.g., UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism) provide the environment to design, test, and deploy bots. A central RPA Orchestrator is critical—it schedules bots, manages credentials securely, distributes workloads, and provides monitoring dashboards.
-
System Integration Layer: This is where RPA interacts with the manufacturing IT stack. Bots use a combination of:
-
Front-End (UI) Automation: For legacy systems without APIs.
-
Back-End (API/Database) Integration: Preferred for modern MES/ERP systems, offering greater robustness and speed.
-
File & Email Handling: To process spreadsheets, PDF inspection reports, and order emails.
-
-
Exception Handling & Human-in-the-Loop (HITL): Robust RPA design includes clear exception pathways. When a bot encounters an unexpected dialog box, missing data, or a value outside pre-set rules, it should escalate the task to a human operator via a dedicated queue with full context, then resume once resolved.
-
Security & Governance: Manufacturing data is sensitive. RPA must adhere to strict governance: secure credential vaults, role-based access control for bots, comprehensive audit logs of every action, and adherence to IT security policies.
4. Quantifying the ROI: From Efficiency Gains to Strategic Advantage
The value of RPA manufacturing is measured in both tangible efficiencies and strategic capabilities.
-
Direct Productivity & Cost Savings:
-
Labor Cost Reduction/Reallocation: Automating manual data entry and administrative tasks can free up 15-30% of an employee’s time, allowing them to focus on analysis, problem-solving, and continuous improvement.
-
Error Cost Elimination: By removing manual handoffs, RPA virtually eliminates costly errors like incorrect purchase orders, wrong shipment details, or misreported production data, which can lead to scrap, rework, and customer penalties.
-
Accelerated Cycle Times: Processes like order-to-production release or inspection reporting can be accelerated from hours/days to minutes, directly improving cash flow and customer responsiveness.
-
-
Enhanced Operational Intelligence & Quality:
-
Improved Data Fidelity & OEE Accuracy: Automated data collection provides a perfect, real-time record of production, enabling accurate OEE calculation and reliable root-cause analysis for downtime.
-
Strengthened Compliance & Traceability: An automated, unbroken digital thread from order to shipment creates an immutable audit trail, drastically reducing the cost and stress of internal and external audits.
-
Empowered Workforce: By removing monotonous tasks, RPA increases job satisfaction and allows the workforce to engage in more skilled, meaningful activities.
-
5. Case Studies: RPA Driving Transformation in Precision Machining
Case Study 1: The High-Mix Job Shop – Automating the Digital Handoff
-
Challenge: A precision job shop with 50+ monthly jobs struggled with a 4-8 hour order processing lag. Engineers manually extracted data from customer RFQ PDFs and emails, entered it into the ERP, then re-keyed details into the CAM system for programming. Errors were frequent, causing incorrect material to be pulled or wrong tools prepared.
-
RPA Solution: JLYPT consultants helped implement a three-bot workflow:
-
Email & PDF Bot: Monitored a dedicated order inbox, extracted part numbers, quantities, and material specs from PDF drawings and RFQs using OCR.
-
ERP Integration Bot: Created the sales order and work order in the ERP system using the extracted data.
-
CAM Launch Bot: Upon ERP work order creation, this bot automatically launched the CAM software, opened the correct part template, and pre-populated fields like material type and stock size.
-
-
Outcome: Order-to-programming lead time reduced to under 30 minutes. Data entry errors fell to zero. Engineers reported a 20% increase in time available for actual CNC programming and process optimization.
Case Study 2: The Aerospace Contractor – Ensuring Unbreakable Traceability
-
Challenge: An AS9100-certified machine shop faced immense pressure during audits. Assembling the digital pedigree for a single flight-critical part involved manually collecting records from 7+ systems: ERP (material cert), MES (operator log), CMM (inspection data), tool logs, and equipment calibration records. This process took a quality engineer 2-3 hours per audit sample.
-
RPA Solution: A “Compliance Auditor Bot” was developed. When provided with a part serial number, the bot would:
-
Query the ERP for the purchase order and material certification.
-
Pull the machine setup sheet and operator from the MES.
-
Retrieve all inspection results from the CMM database.
-
Fetch tool usage and calibration records for the tools used.
-
Compile everything into a single, time-stamped, bookmarked PDF file.
-
-
Outcome: The audit packet compilation time dropped from hours to 5 minutes. The shop achieved a reputation for flawless audit readiness, reduced QA overhead costs, and provided customers with instant traceability reports, enhancing trust and enabling bids for more sensitive work.
Case Study 3: The High-Volume Automotive Supplier – Real-Time Production Control
-
Challenge: A plant running three shifts had a lag of one full shift in its OEE reporting. Supervisors used clipboards, leading to inaccurate downtime reason coding. Production adjustments were always reactive, based on yesterday’s data.
-
RPA Solution: An RPA bot was deployed alongside a basic machine monitoring sensor. Every 15 minutes, the bot:
-
Logged into the HMI of each of 30 CNC machines (via virtual desktop) and scraped the cycle counter and alarm history.
-
Compared the count to the expected rate, classifying the machine as Running, Idle (Starved/Blocked), or Down.
-
For “Down” states, it read the most recent alarm code and mapped it to a standard downtime reason.
-
Pushed this classified data in real-time to a cloud-based dashboard visible to floor managers and plant leadership.
-
-
Outcome: The plant achieved real-time OEE visibility. Supervisors could now respond to bottlenecks as they occurred. Downtime reason accuracy improved from ~60% to 98%, enabling targeted maintenance improvements. Overall plant capacity increased by 5% within three months simply by addressing the largest, newly visible bottlenecks.
6. The Future: From RPA to Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) in Manufacturing
RPA manufacturing is the foundational step towards Intelligent Process Automation (IPA). The next evolution involves integrating RPA with cognitive technologies:
-
Computer Vision (CV): Bots will be able to “read” complex engineering drawings, identify part features, and validate fixture setups from camera images.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Bots will process unstructured work instructions or customer emails to automatically generate action items or update orders.
-
Process Mining & AI: AI will continuously analyze bot-executed processes to discover further optimization opportunities, predict process failures, and dynamically adjust bot workflows for maximum efficiency.
Conclusion: Building the Cognitive Factory Floor
In the competitive world of precision CNC machining, excellence is no longer defined solely by the capabilities of the machine tool. It is defined by the intelligence, speed, and resilience of the digital ecosystem that supports it. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) manufacturing is the key to building this ecosystem. It provides a pragmatic, powerful, and non-disruptive path to connect siloed systems, eliminate costly administrative friction, and create a seamless digital thread that enhances every aspect of production—from the first customer inquiry to the final shipped part.
At JLYPT, we understand that true manufacturing excellence lies at the intersection of physical precision and digital fluency. We partner with our clients not only to produce intricate components but also to engineer the smart, automated digital workflows that make their entire operation more agile, reliable, and data-driven. Implementing RPA manufacturing is a strategic decision to empower your human talent, protect your margins from hidden administrative costs, and build a foundation for the cognitive factory of the future.
Ready to automate the digital backbone of your machining operations and unlock new levels of efficiency? Explore how JLYPT’s expertise in precision manufacturing and digital transformation can help you design and implement a winning RPA manufacturing strategy. Begin the conversation by visiting our comprehensive service page at JLYPT CNC Machining Services.