Rapid 3D Printing Services
Precision, Speed, and Custom Solutions—All in One Place
3D Printing Technologies
JLYPT offers high-quality additive manufacturing services, including FDM, SLA, SLS, and SLM, enabling fast, precise 3D printing in plastics and metals. Ideal for rapid prototyping, functional parts, and low-volume production, our solutions handle complex geometries that traditional methods can’t achieve.
Affordable for basic prototypes
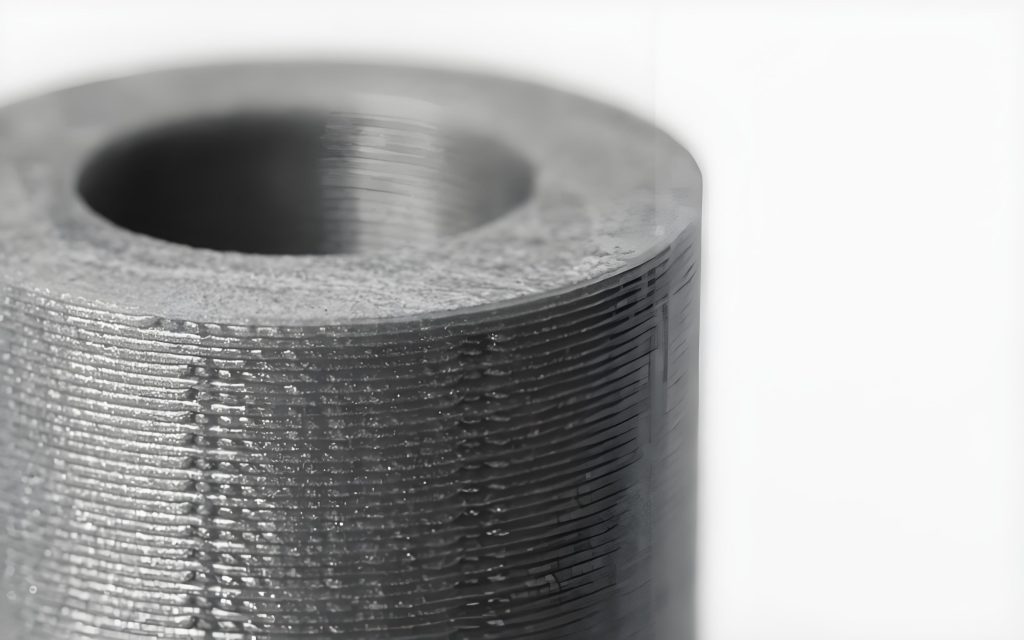

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the most widely used additive manufacturing process for desktop 3D printers. The process extrudes melted plastic from a computer-controlled nozzle, building a part layer by layer.
FDM 3D printers use a spool of filament as raw material. This filament is directed into the print head, where it is melted and deposited onto the incomplete part. By computer instructions, the print head moves along 3 axes to deposit material in the right place.
Because the material cools after it is deposited, further layers of material can be deposited on top of the existing layers, allowing for the creation of 3D shapes. FDM is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
Visual prototype
Stereolithography (SLA) is an additive manufacturing process that works differently way to FDM. In SLA 3D printing, a 3D object is created with a laser, which is directed at areas of photosensitive liquid resin. The laser causes areas of the resin to harden, forming a solid part.
The process takes place in a tank of liquid resin, where a build platform moves vertically after each layer is cured. The laser is precisely guided using a system of mirrors to target specific areas of the resin surface. This layer-by-layer curing method enables exceptional accuracy, fine details, and smooth surface finishes.
While SLA is limited to photopolymer materials, it’s ideal for highly detailed prototypes and small functional parts. First introduced in the 1980s, SLA is now a well-established and widely trusted additive manufacturing technology.
Functional prototyping and low-volume parts
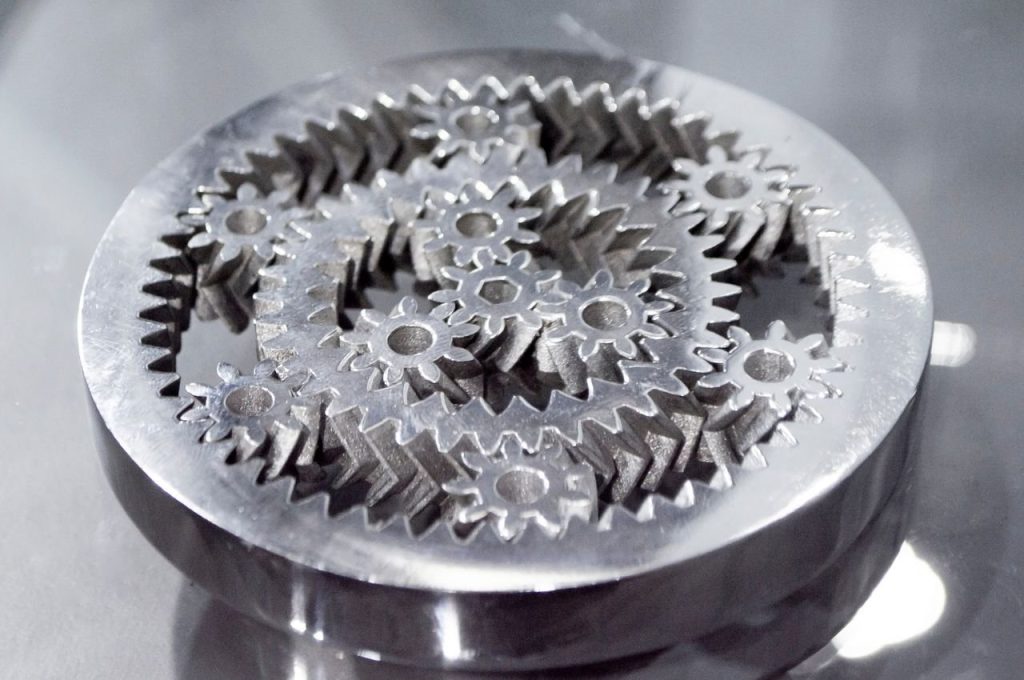
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a powder bed additive manufacturing process used to make parts from thermoplastic polymer powders. It is commonly used for functional parts, since SLS printed components have good mechanical properties.
An SLS 3D printer works by sintering areas of plastic powder with a laser. During the process, a thin layer of powder is distributed evenly across the build platform, after which the laser sinters selected areas of the 2D layer. When the layer is complete, the platform is lowered, more powder is added, and the laser sinters the next layer.
When all layers are complete, the part is left to cool. Unused powder is kept to be used again, and the part is cleaned to remove excess material.
Parts for functional end use

Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is a metal 3D printing process that builds high-strength parts layer by layer from fine metal powder. Inside a sealed, inert gas-filled chamber, a powerful laser selectively melts the powder based on the cross-sections of a CAD model. Once a layer is completed, the build platform lowers slightly, and a fresh layer of powder is spread across the surface to continue the build.
Unlike sintering processes, SLM fully melts the metal powder, resulting in parts with excellent mechanical properties and near-wrought strength. This makes it suitable for highly demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, medical, and more. The technology also allows for the production of complex geometries, internal channels, and lightweight structures that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing.
Jly offers a wide range of materials and applications to support your projects
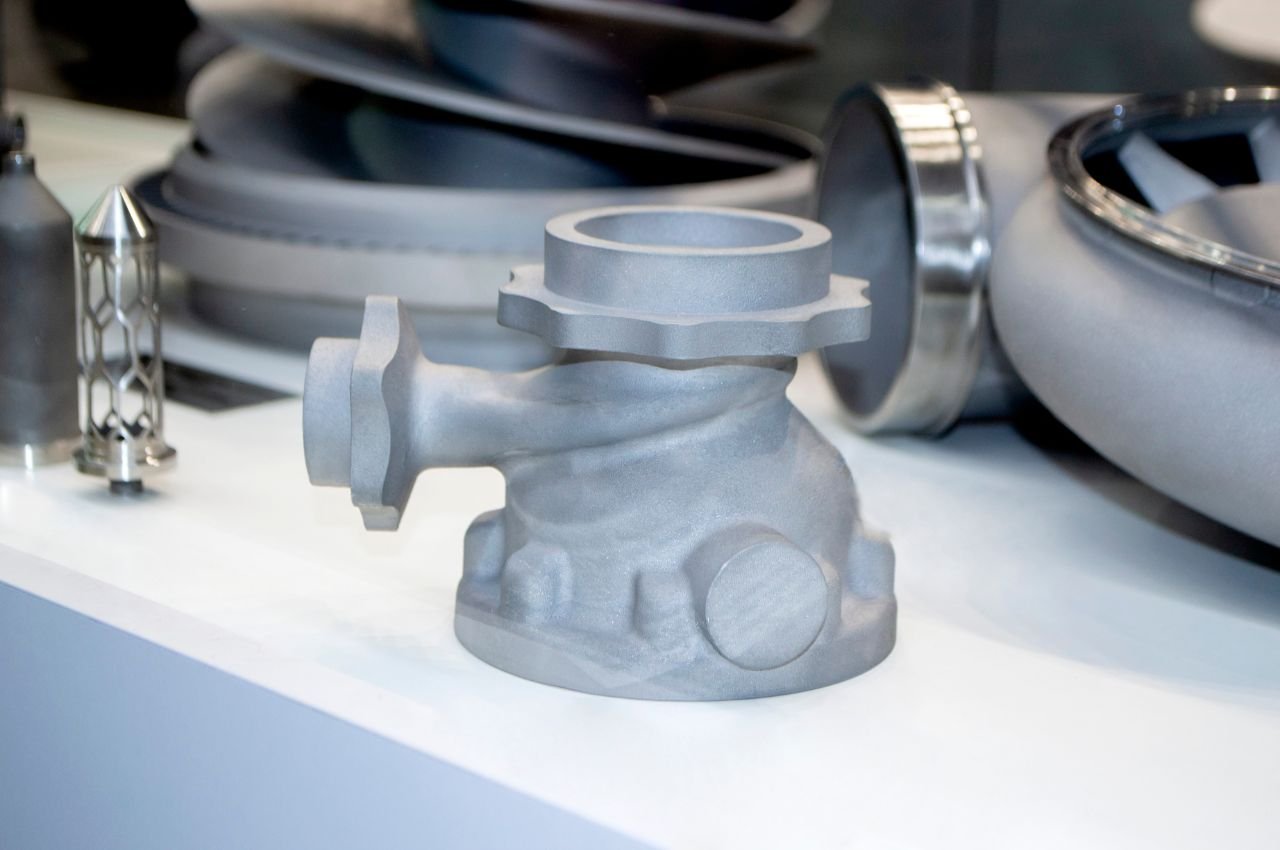

Rapid prototyping for new products.
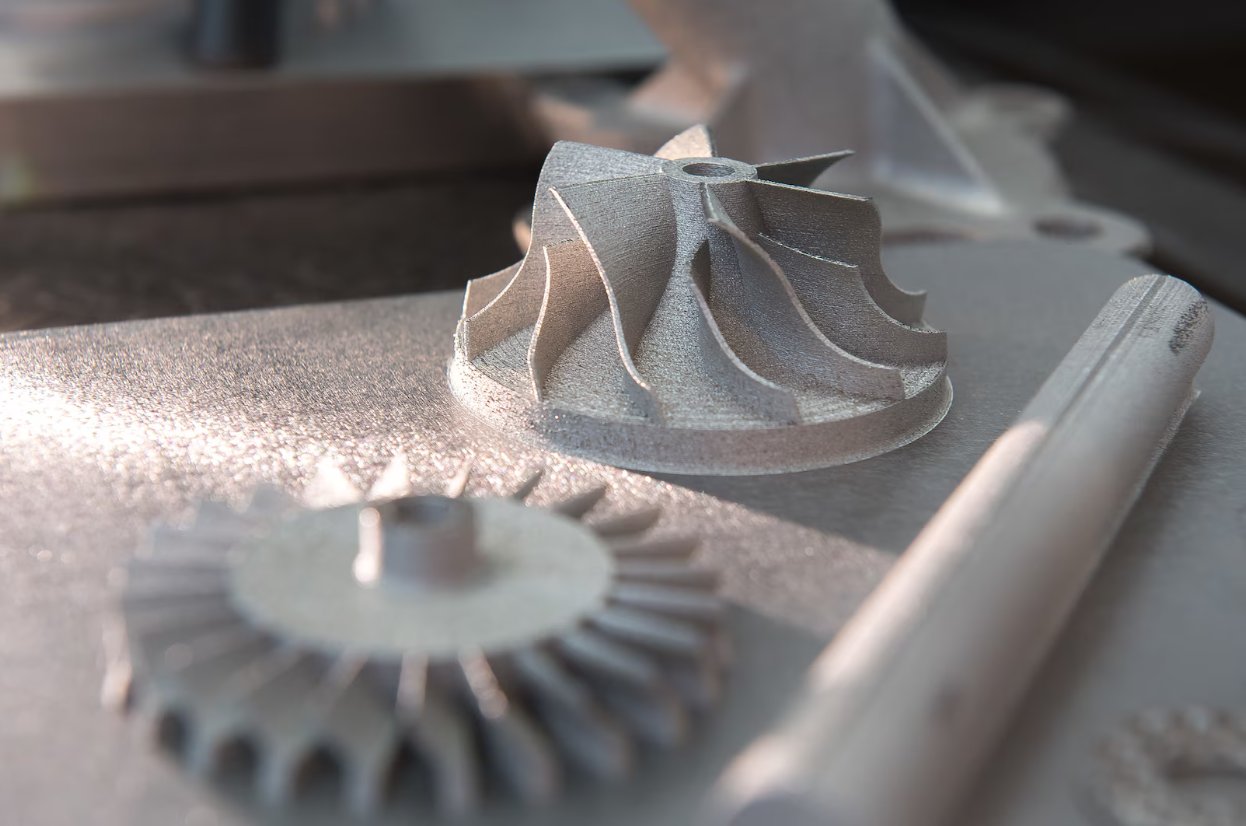

Lightweight components and test models.
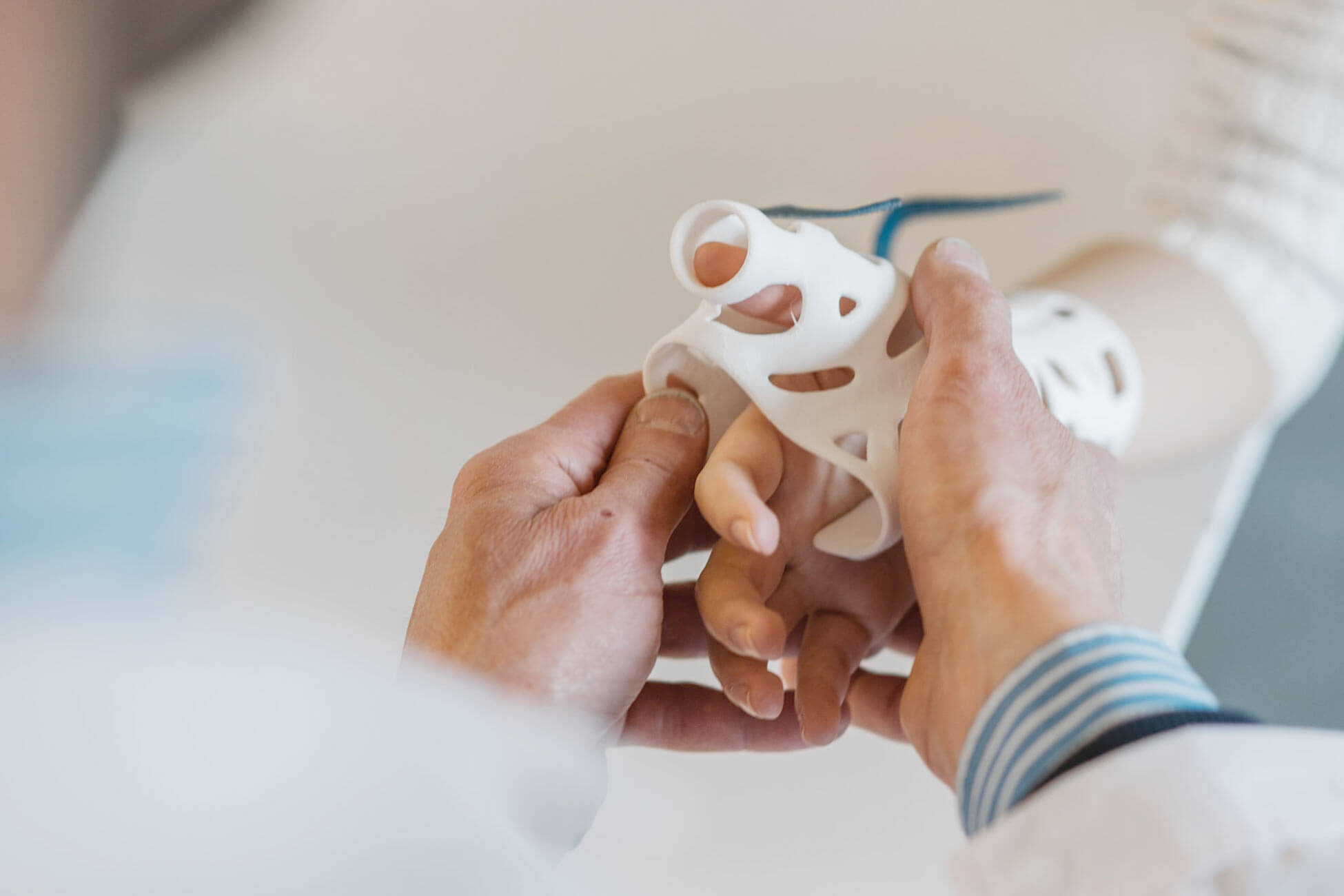

Custom prosthetics and surgical tools.
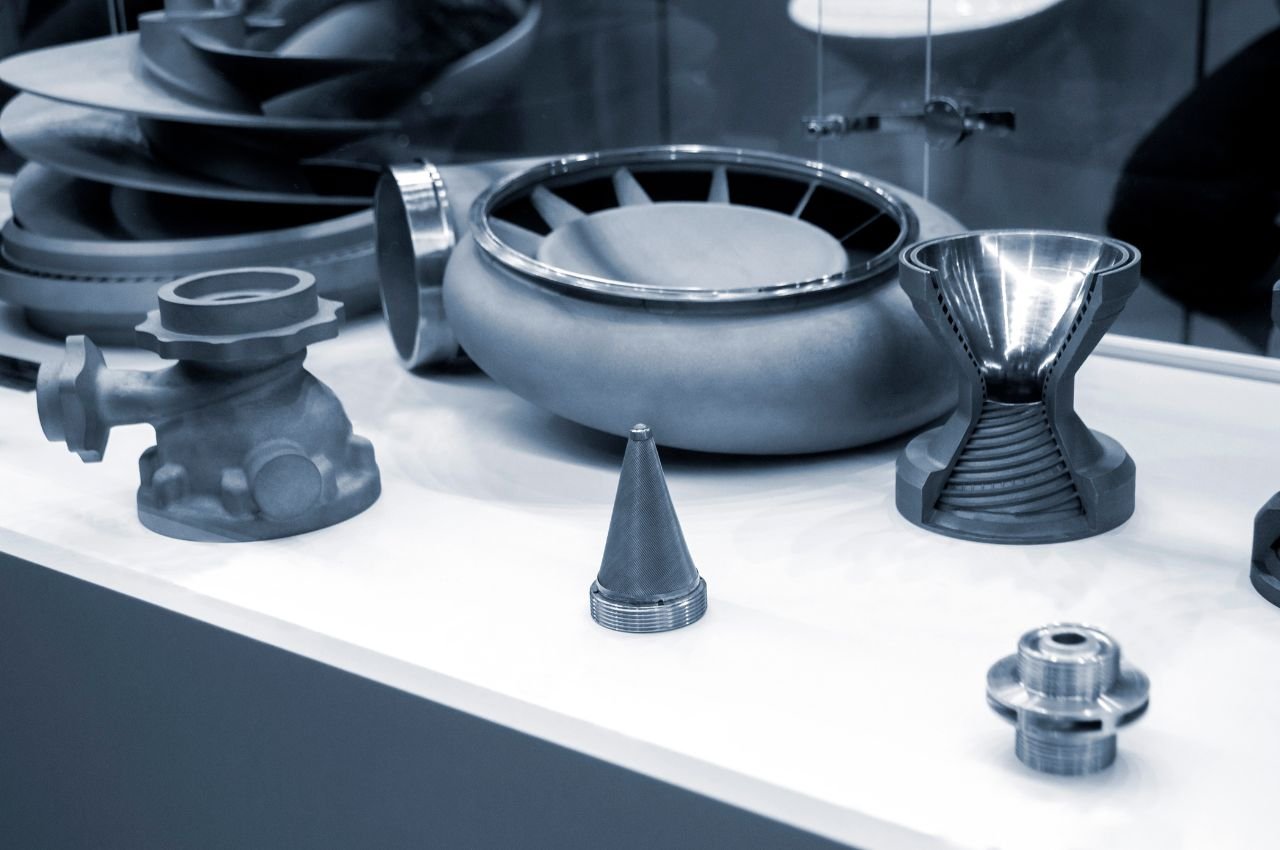

Jigs, fixtures, and production prototypes.
- Thermoplastics: PLA, ABS, PETG (strong and cost-effective).
- Photopolymers: Flexible, High-Temperature, Clear Resins (for SLA).
- Advanced Options: Nylon, TPU, Metal Alloys (via SLS or hybrid).
Select the Ideal 3D Printing Technology
Unsure which method suits your project? This comparison helps—consult our experts for guidance!
| Feature | FDM | SLA | SLS |
| Materials | PLA, ABS, Nylon | Resins (Tough, Clear) | Nylon, TPU, Metal Powders |
| Applications | Prototypes, Housings | Jewelry, Dental Models | Gears, Functional Parts |
| Layer Thickness | 0.1–0.3mm | 0.025–0.1mm | 0.06–0.12mm |
| Build Volume | 400x400x500mm | 300x300x400mm | 340x340x600mm |
| Best For | Cost-Effective Prototyping | High-Detail Applications | Durable, Complex Designs |
Enhance Your 3D Printing Outcomes
Use STL or STEP with solid models.
Keep walls at least 1.5mm thick.
Add supports for angles over 45°.
Request sanding or painting for a polished look.
Engineered for Speed and Quality
FDM, SLA, and SLS,SLM printers.
Zeiss CMM for precision checks.
Deliveries in as little as 24 hours.
Custom solutions for your designs.
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining: Which is Better for Your Prototypes and Production?
Understanding 3D Printing and CNC Machining
3D printing and CNC machining are two powerful manufacturing technologies, each with distinct strengths. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, excels in producing small batches of parts without the need for molds, allowing for rapid turnaround and low costs. It requires minimal human intervention, enabling automated production. The cost of 3D printing is determined by the amount of material used, meaning larger parts or higher quantities can increase expenses. On the other hand, CNC machining, a subtractive process, is more complex. It requires specially trained engineers to pre-program machining parameters and tool paths, followed by automated production based on those instructions. This preparation adds labor costs to the quotation, but CNC machines can operate continuously without supervision, making them highly suitable for large-scale production.
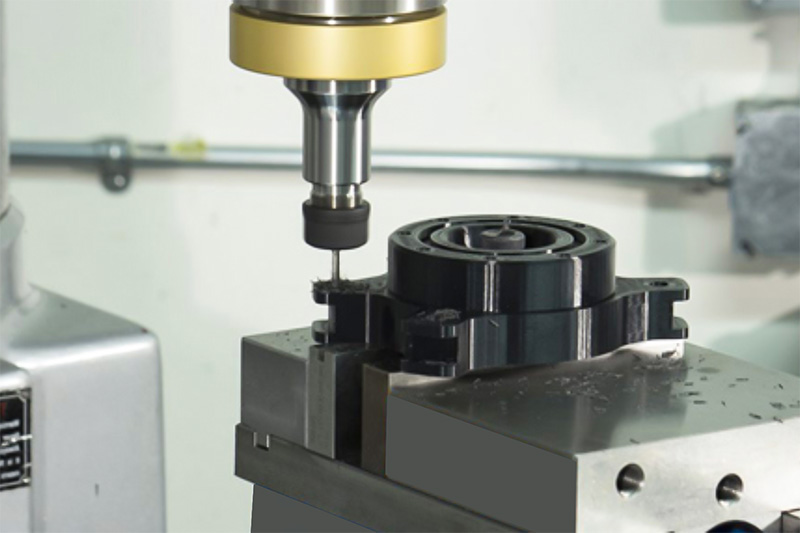

Comparing 3D Printing and CNC Machining
Here’s a detailed comparison to help you decide which technology best fits your prototyping or production needs:
Feature | 3D Printing (Additive) | CNC Machining (Subtractive) |
Process | Builds layer by layer from digital designs | Cuts material from a solid block |
Materials | Plastics, Resins, Metals (limited) | Metals, Plastics, Composites (wide range) |
Speed | Fast for prototypes (24–48 hours) | Slower setup, better for high volumes |
Cost | Low for small runs, rises with material use | High setup, cost-effective for mass production |
Complexity | Ideal for complex geometries | Limited by tool access |
Finish | May need post-processing | High-quality finish out of the box |
Best For | Prototypes, custom parts, low-volume production | High-precision, large-scale production |
When to Choose 3D Printing: Opt for 3D printing with Jly for rapid prototypes, intricate designs, or small batches. Our FDM, SLA, and SLS technologies deliver parts in as little as 24 hours, perfect for iterative design and testing.
When to Choose CNC Machining: Select CNC machining for high-volume production or parts requiring superior surface finish and tight tolerances. Jly offers CNC services for projects needing durability and scale.
Hybrid Approach: Combine both for optimal results—use 3D printing for initial prototypes and CNC for final production runs. Contact our experts to find the best fit!
Popular Materials
JLY offers a wide selection of popular metal and plastic materials, including Aluminum, Stainless Steel, and Nylon—ideal for a variety of custom 3D printing projects. Have specific material needs? Contact us anytime, and we’ll get back to you within 12 hours.
| Color: | Silver |
| Alloys: | Aluminium 7075-T651 | 3.4365 | 76528 | AlZn5.5MgCu Aluminium 6082-T651 | 3.2315 | 64430 | AlSi1MgMn Aluminium 6060 | 3.3206 | AlMgSi Aluminium 5052 | EN AW-5052 | 3.3523 | AlMg2,5 Aluminium 2017 | 3.1325 | 24530 | AlCu4MgSi |
| Available Finish: | As machined, Anodizing, Powder coating, Electroplating, Painting, Sand blasting, Polishing |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

Stainless steel, printed via SLM/DMLS, delivers high strength and corrosion resistance for tooling, medical devices, and mechanical parts.
| Color: | Silver |
| Alloys: | Stainless steel 416 | 1.4005 | X12CrS13 Stainless steel 15-5 | 1.4545 | X5CrNiCu15-5 Stainless steel 301 | 1.4310 | X10CrNi18-8 Stainless steel 430 | 1.4016 | X6Cr17 Stainless steel 440C | 1.4125 | X105CrMo17 Stainless steel 420 | 1.4028 | X30Cr13 Stainless steel 304/304L | 1.4301/1.4307 | X5CrNi18-10/X2CrNi18-9 Stainless steel 2205 Duplex | 1.4462 | 2205 | X2CrNiMoN 22-5-3 Stainless Steel 17-4 PH | 1.4542 | X5CrNiCuNb16-4 – Annealed state Stainless steel 303 | 1.4305 | X8CrNiS18-9 Stainless steel 316/316L | 1.4401/1.4404 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2/X2CrNiMo17-12-2 |
| Price: | $$$ |
| Lead Time: | About 7 business days |

Titanium
Titanium is ideal for SLM/DMLS 3D printing, combining high strength, low weight, and biocompatibility—perfect for aerospace and medical implants.
| Color: | Silver |
| Alloys: | Titanium Grade 5 | 3.7164 | Ti6Al4V Titanium Grade 2 | 3.7035 Titanium Grade 1 | 3.7025 |
| Price: | $$$$$ |
| Lead Time: | About 8 business days |
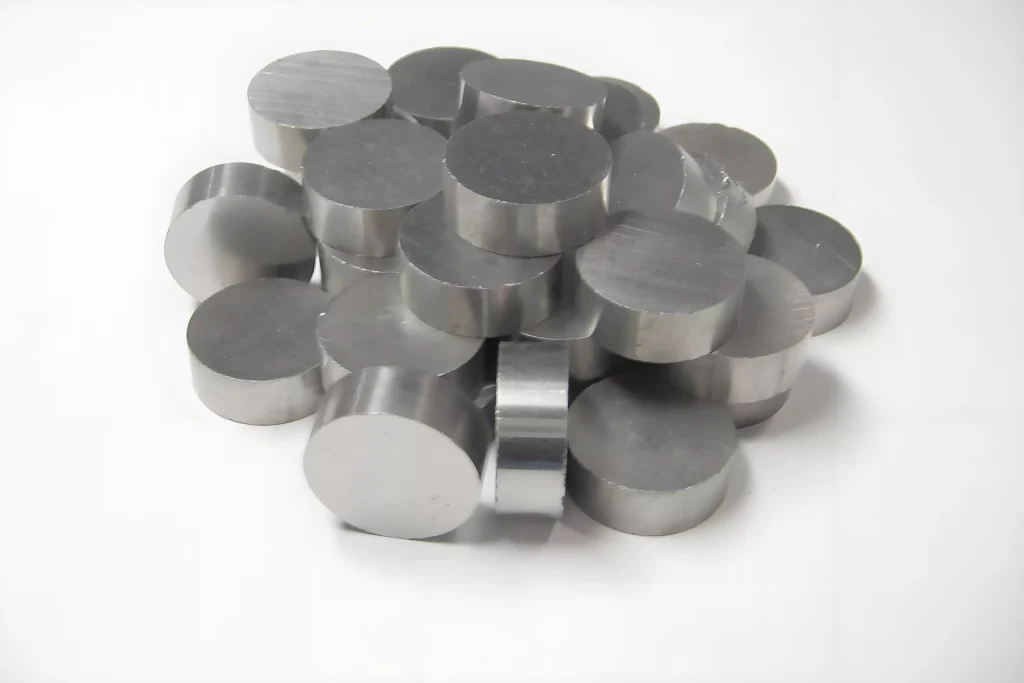

Titanium
Inconel can be used for SLM/DMLS. Excels in high-heat, corrosive environments, making it suitable for turbines and extreme-temperature components.
| Color: | Silver |
| Alloys: | Inconel 601, Inconel 625, Inconel 718 As machined, Polishing, Sand Blasting, Tumbling, Alodine, Heat treatment, Anodizing, Teflon coating, Electroless nickel, Painting, Powder coating, Electrophoresis |
| Price: | $$$$$ |
| Lead Time: | About 8 business days |

ABS
ABS can be used for FDM, offering durability, impact resistance, and machinability—ideal for functional prototypes and mechanical parts.
| Color: | Light Beige – Black |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

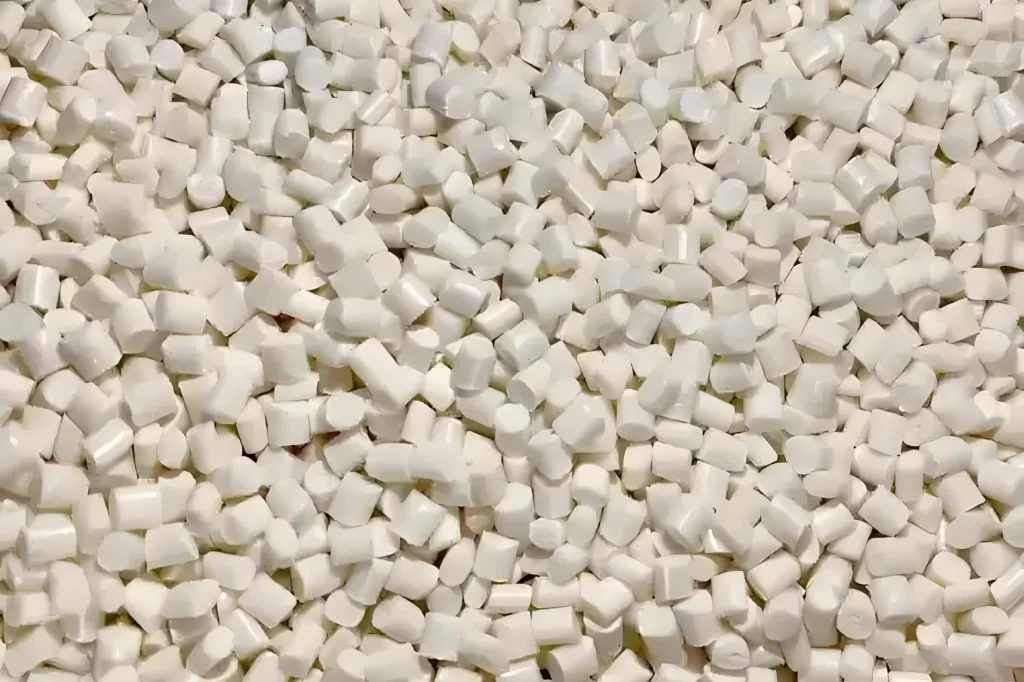
PA(Nylon)
Nylon (PA) is used in SLS/FDM, providing strength, flexibility, and wear resistance for enclosures, gears, and end-use components. Aluminium-filled nylon provides high stiffness and a metallic appearance.
| Color: | White |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

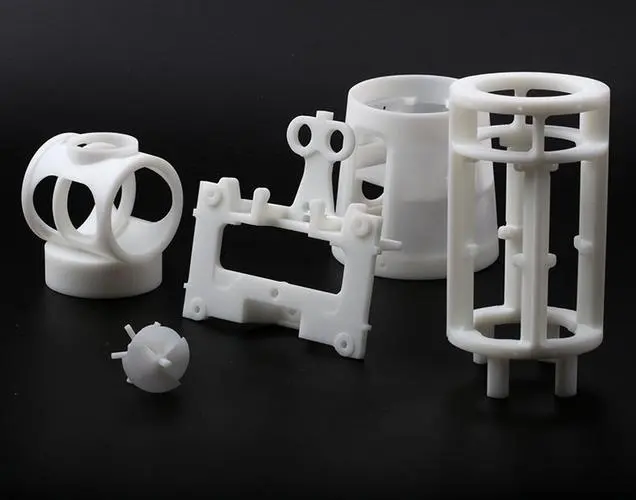
Resin
Resin is a liquid photopolymer plastic used in 3D printing, ideal for high-detail prototypes with smooth surfaces and fine features. The common subtypes include Resin 8119, 8118H, 8228, and 8338.
| Color: | White – Colors |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

Resin
Resin is a liquid photopolymer plastic used in 3D printing, ideal for high-detail prototypes with smooth surfaces and fine features. The common subtypes include Resin 8119, 8118H, 8228, and 8338.
| Color: | White – Colors |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

PC
Polycarbonate (PC) can be used for FDM, combining excellent strength and heat resistance—perfect for tooling, fixtures, and load-bearing parts.
| Color: | White – Black |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 6 business days |

PETG
PETG is used for FDM. It is easy to print and chemical-resistant, ideal for containers, housings, and functional prototypes.
| Color: | White – Colors |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

PEEK
PEEK can be used for FDM, delivering outstanding mechanical and chemical performance for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications.
| Color: | White |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

PEI
PEI (Ultem) is a flame-retardant thermoplastic used in FDM, offering high strength and thermal stability for electrical and structural components.
| Color: | Orange |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |

PPSU
PPSU can be used for FDM, providing exceptional toughness and sterilizability—ideal for medical and aerospace environments.
| Color: | Black |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 6 business days |

PMMA (Acrylic)
PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) is used in SLA or DLP 3D printing for high-clarity, rigid parts that simulate glass in optical or display applications.
| Color: | Black – White |
| Price: | $ |
| Lead Time: | About 6 business days |

PLA
PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic used in FDM, offering ease of printing, good surface finish, and low warping—ideal for prototypes and models.
| Color: | White – Colors |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 5 business days |
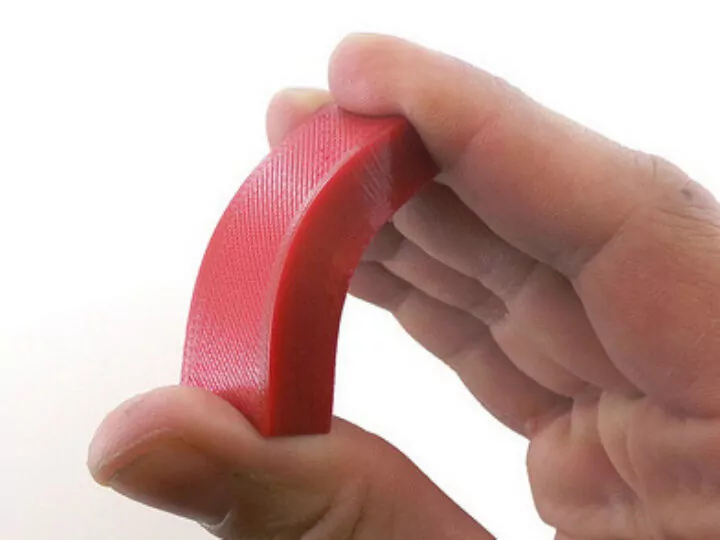

TPU/TPE
TPU/TPE are flexible materials that can be used for FDM. It is a highly elastic material with high tear and abrasion resistance, as well as satisfactory thermal resistance.
| Color: | White – Colors |
| Price: | $$ |
| Lead Time: | About 6 business days |
Your Rapid 3D Printing Partner
Need fast, precise parts? Jly’s rapid 3D printing services deliver with unmatched efficiency. Let’s bring your vision to life!

